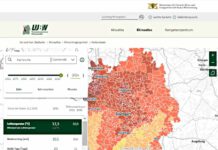
© Double rainbow (DI01454), University Corporation for Atmospheric Research, Photo by Carlye Calvin
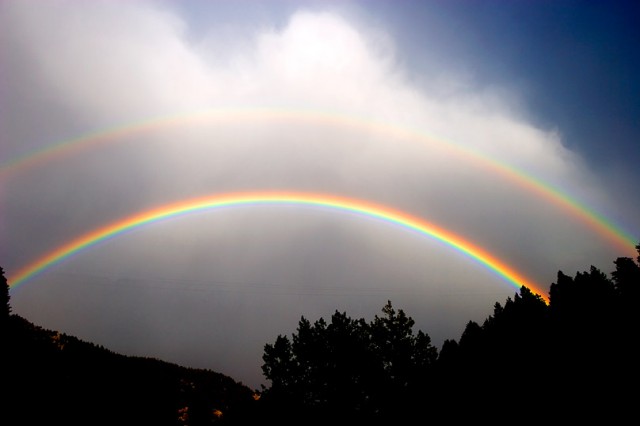
© Double rainbow (DI01454), University Corporation for Atmospheric Research, Photo by Carlye Calvin
When direct sunlight strikes falling rain, a rainbow is seen at a point directly opposite the Sun. A double rainbow occurs when some of the light entering the raindrop is refracted into its component colors, reflected off the back interior wall of the drop, and refracted again as it exits the drop. The dark area inbetween the two rainbows is called Alexander’s band